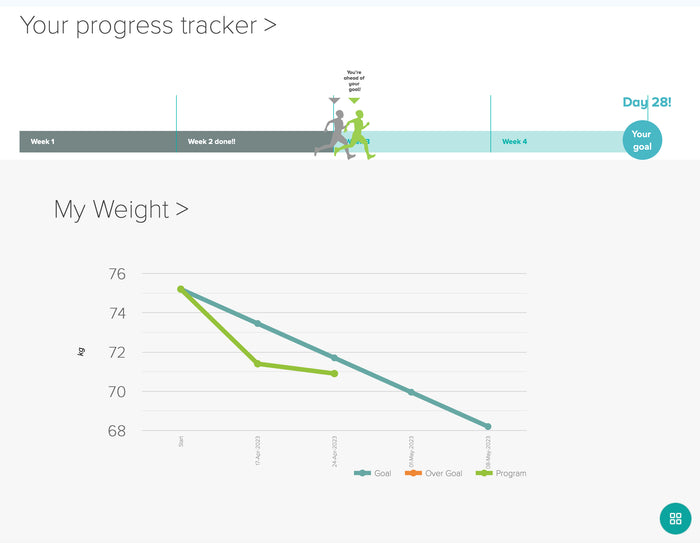
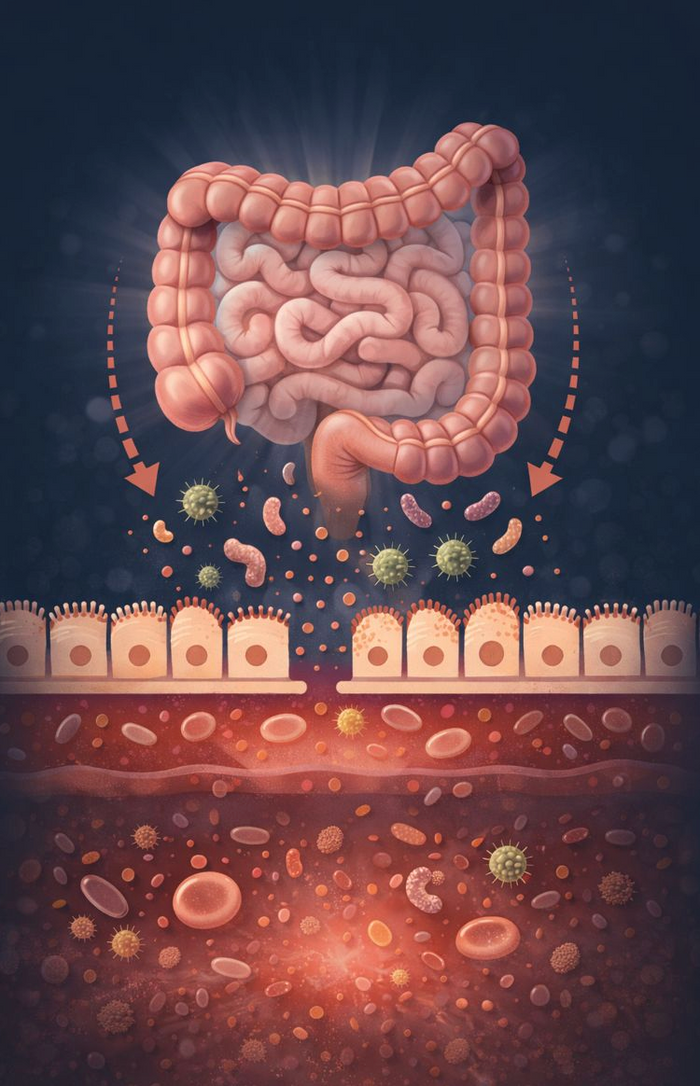
There is bacteria naturally living in the gut of humans which helps us to digest food. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) is a condition where the gut bacteria that normally populates our large intestine, relocates to the small intestine where large amounts of bacteria are not normally present.
Symptoms can include:
- Bloating
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhoea and/or constipation
- Cramps
- Nausea
- Altered mood and energy levels
SIBO has been shown to negatively affect both the structure and function of the small bowel, which may contribute to leaky gut. Leaky gut refers to when the lining of the gut wall become permeable and large protein molecules escape into the blood stream. This can result in inflammation, food allergies, food intolerances and auto immune diseases. SIBO may also inhibit the body’s ability to digest food and absorb nutrients.
Like most gut disorders, there is no single cause of SIBO, however, risk factors may include irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, diabetes, coeliac disease and overuse of antibiotics.
The most common treatment for SIBO is a course of antibiotics, with more than one variety of antibiotics often being used. This treatment works to directly reduce the amount of bacteria present in the small intestine.
Another option that may be used alone or in conjunction with antibiotic treatment is to follow a specific diet that excludes the components of food that the bacteria feed off. This diet may be a ‘Specific Carbohydrate Diet’ or a ‘Low Fodmap Diet’, or you may follow a combination of the two. By reducing the fermentable components that bacteria feed off, you are essentially starving the bacteria, resulting in a reduced number. Dietary modification has been shown to provide relief to the majority of people with SIBO.
What does the ‘Specific Carbohydrate Diet’ allow?
The focus is to exclude starchy and fermentable carbohydrates, while allowing insoluble fibre from other food sources to promote bowel health.
Foods allowed:
- Meat, fish, poultry
- Non starchy vegetables
- Ripe fruits
- Nuts and seeds
- Eggs
- Lactose free dairy
Foods not allowed:
- Most starchy vegetables
- Most grains and products derived from grains including wheat and wheat flour, barley, rye, oats, rice
- Some beans/legumes
For further information on identifying and/or managing SIBO, please contact support@astonrx.com