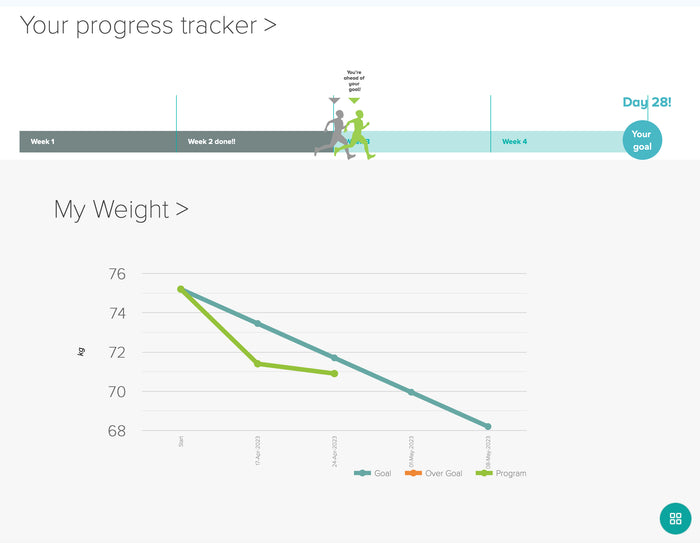
What are antibiotics?
Antibiotics are used to treat and prevent bacterial infections. The antibiotic prescribed can either be broad spectrum (kills a range of bacteria) or only target a specific bacteria. Majority of individuals would have had to use antibiotics at some stage in their lives. Due to the nature of antibiotics they do not only just treat the bacteria that causes the infection they can also impact the good bacteria in the gut that plays an important role in supporting health.
Effects of antibiotics on gut health
Antibiotic use effects the bacteria in the gut by reducing diversity. The disrupted gut microbiota increases the risk of inflammatory bowel diseases, diabetes, obesity as well as infection inside and outside the gut. Studies have shown that after only one week of antibiotic use it can take the gut flora up to 12 months to recover!
How to minimise antibiotic impact on gut health
During antibiotic use try to be consistent with dietary fibre and include nuts, seeds and fibrous plant foods that can feed the bacteria in the gut and consider the use of a probiotic which may help support gut health. Studies have shown that taking probiotics can help reduce diarrhoea induced by antibiotic use and possibly restore the microbiome post antibiotic use.
When taking a probiotic it is best to choose one with multiple strains and to leave a few hours in between taking an antibiotic and a probiotic. As a general rule wait a minimum of 2 hours to allow the antibiotic to work but not kill any of the beneficial bacteria in the probiotic.