Have you ever noticed that when you're stressed, your digestive system feels off, or you may even gain weight? It's not a coincidence! The connection between physical and emotional stress and our overall health, gut health, weight, and longevity is fascinating. In this blog, we'll explore how stress impacts these aspects of our lives and provide actionable tips for a healthier and more balanced lifestyle.
Understanding the Impact of Stress
Stress, whether physical or emotional, triggers a physiological response in our bodies. When we stress, our adrenal glands release cortisol and adrenaline - the "fight or flight" hormones. However, chronic stress and prolonged exposure to stress hormones can wreak havoc on our health.
Gut Health and Stress
The gut, often referred to as our second brain, plays a significant role in our overall well-being. When we're stressed, the balance of beneficial and harmful bacteria in our gut can be disrupted. This imbalance can lead to digestive issues, weakened immune function, and even contribute to the development of chronic conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
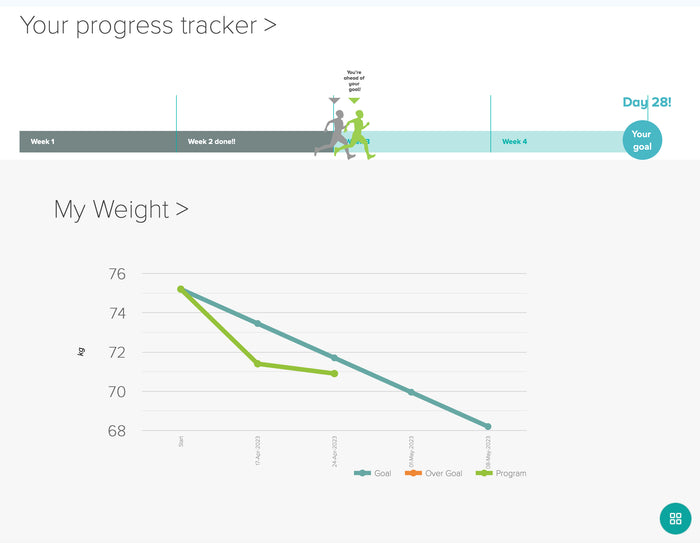
Weight and Stress
Stress can also impact our weight. When stress hormones are elevated, our bodies respond by conserving energy and increasing fat storage, particularly around the abdominal area. Additionally, stress can trigger emotional eating or cravings for sugary, high-fat, and processed foods, which can further contribute to weight gain.
Longevity and Stress
The accumulation of stress over time can accelerate the aging process and reduce our overall lifespan. Chronic stress increases inflammation in the body, which is associated with a higher risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. By managing stress effectively, we can improve our overall health and potentially extend our longevity.
Tips for Managing Stress:
1. Prioritise Self-Care: Engage in activities that bring you joy and relaxation, such as practicing mindfulness, engaging in hobbies, or spending time in nature. Taking time for yourself is vital for reducing stress levels.
2. Regular Exercise: Physical activity releases endorphins, the feel-good hormones that can counteract the effects of stress. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week to promote overall well-being.
3. Healthy Eating: Opt for a balanced diet, incorporating a diverse range of fibrous plant foods, high-quality protein and unrefined fats and oils. These foods provide essential nutrients that support overall health, including gut health. Avoid excessive consumption of processed and sugary foods, which can contribute to inflammation and weight gain.
4. Restful Sleep: Prioritise quality sleep by establishing a consistent sleep routine and creating a peaceful sleep environment. Adequate rest supports both mental and physical resilience to stress.
Physical and emotional stress can significantly impact our overall health, gut health, weight, and longevity. By understanding the connection between stress and these aspects of our lives, we can take proactive steps towards stress management and a healthier lifestyle. Prioritise self-care, practice good dietary habits, engage in regular physical activity, and foster restful sleep to reduce the negative effects of stress. Remember, small changes can have a big impact on our overall well-being and promote a happier, healthier life.