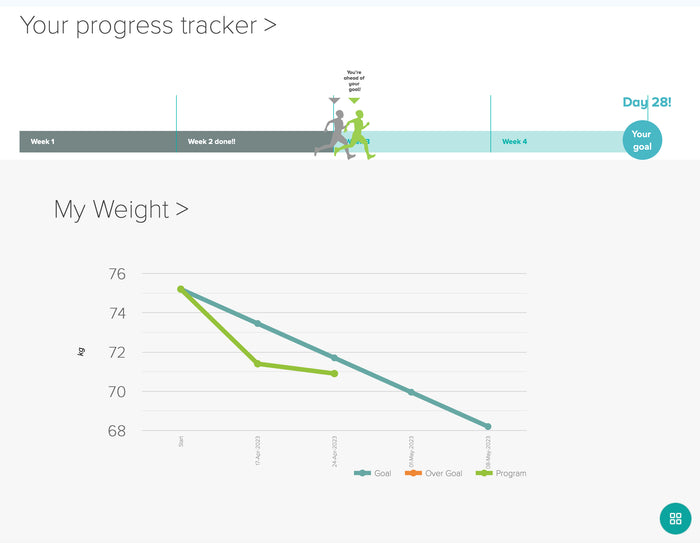
Emotional eating is a common response to stress, anxiety, or boredom, leading to overeating and weight gain.
However, through awareness and adopting healthy coping mechanisms, it is possible to overcome this habit. In this blog, we will explore tips to identify emotional eating patterns and effective strategies to manage them.
Monitor your triggers: Keep a food diary and note down your emotions before and after eating. Recognise patterns where certain emotions trigger your desire to eat excessively.
Distinguish between emotional hunger and physical hunger: Emotional hunger comes on suddenly and will lead to cravings for specific comfort foods. Physical hunger, on the other hand, develops gradually and can be satisfied by any type of food.
Pay attention to your thought process: Notice if you find yourself reaching for food as a response to stress, sadness, or anxiety. Emotional eating often involves mindless eating, where you consume food without being hungry.
Assess past emotional eating episodes: Reflect on instances where you had a strong emotional reaction and how it influenced your eating habits. Look for patterns to better understand what triggers emotional eating episodes.
Managing Emotional Eating
1. Develop alternative coping mechanisms: Find activities that provide solace and help relieve emotional stress. Engaging in activities such as exercise, meditation, journaling, or pursuing a hobby can divert your attention from food.
2. Build a support system: Reach out to friends, family, or a support group to discuss your struggles with emotional eating. Surrounding yourself with understanding and supportive individuals can offer guidance and encouragement.
3. Practice mindful eating: Focus on listening to your body's hunger cues and eating when you are truly hungry. Slow down while eating, savour each bite, and pay attention to the flavours and textures of your food. This helps you become more conscious of your food choices and prevent mindless snacking.
4. Create a balanced meal plan: Opt for a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutritious foods to keep your body nourished. Include protein, fibre, and healthy fats to help regulate blood sugar levels and keep you fuller for longer.
5. Seek professional help if needed: If emotional eating becomes a persistent issue that affects your physical and mental health, consider seeking support from a psychologist who can guide you through personalised strategies and therapies.
Emotional eating can be a challenging habit to break, but with awareness, self-reflection, and the adoption of healthy coping mechanisms, it is possible to regain control over your eating habits.
By implementing these tips, you can achieve a healthier relationship with food and gain emotional well-being.